Aluminum alloys: an industrial all-rounder and a new chapter in welding technology introduction
2024-04-17 14:35:09
In the rapid development of modern industry, aluminum alloy has become an indispensable structural material in many fields due to its unique light weight, high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. From aircraft soaring in the sky to cars driving on the road, from sophisticated mechanical equipment to consumer electronics used daily, aluminum alloys are used everywhere, and their demand is growing with the booming industrial economy. This article will take an in-depth look at the classification and properties of aluminum alloys and the latest advances in welding technology, revealing the unlimited potential of this industrial all-rounder.
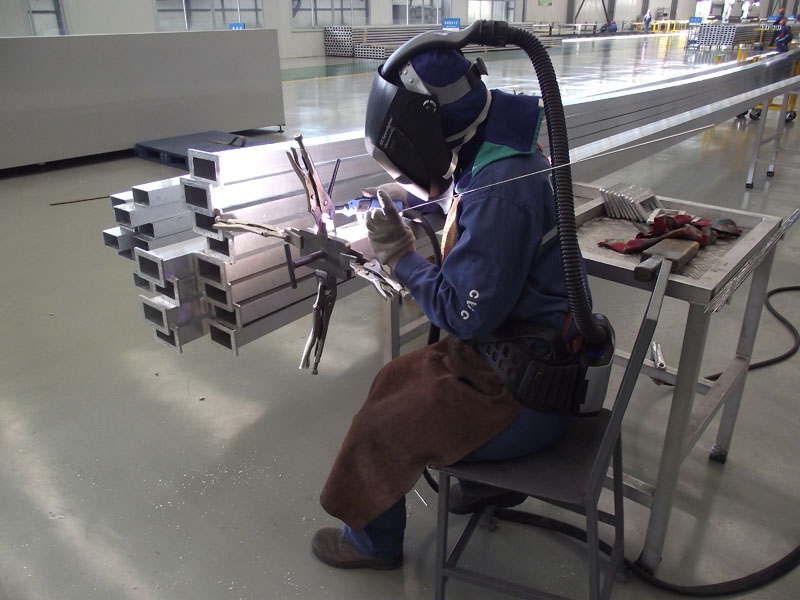

Classification and characteristics of aluminum alloys
2.1 The secrets of various aluminum alloys
The alloy grade of aluminum alloy is like an ID card. Behind the four digits are different alloy compositions and characteristics, providing diversified choices for different industries:
1XXX series: Representative of pure aluminum. The high purity gives them excellent plasticity and conductivity, making them ideal for the electrical and food industries. Their high purity not only ensures the purity of the materials, but also gives them more flexibility in chemical treatments and surface treatments.
2XXX series: The addition of copper elements significantly improves the hardness and strength of this series of aluminum alloys, making it the preferred material for aviation equipment. These alloys perform well in withstanding heavy loads and high-strength working environments and are indispensable structural materials in the aerospace industry.
3XXX series: The incorporation of manganese element gives the aluminum alloy good anti-rust ability, allowing it to maintain stable performance in humid environments. These materials are widely used in home appliances, car radiators and architectural decoration, and their rust-proof properties provide designers with more choices.
4XXX series: The addition of silicon element enhances the welding performance and thermal stability of aluminum alloy, making it the first choice for welding materials and heat-resistant parts. These alloys play an important role in automobile engines, chemical equipment, and kitchen appliances, and their superior welding properties bring convenience to the manufacturing industry.
5XXX series: The doping of magnesium makes this series of aluminum alloys outstanding in corrosion resistance and weldability. They are frequently used in ship and vehicle manufacturing. The materials’ marine-grade corrosion resistance makes them preferred in the shipbuilding industry, while also playing an important role in vehicle lightweighting.
6XXX series: The combination of magnesium and silicon gives this series of aluminum alloys excellent mechanical properties and processability, and is widely used in automobile and furniture manufacturing. These alloys have excellent processing properties and can be easily cut, formed and welded, providing designers and engineers with a broad design space.
7XXX series: The addition of zinc brings the strength and hardness of aluminum alloys to their peak, allowing them to play a key role in the aviation and military fields. These ultra-high-strength aluminum alloys are indispensable in applications requiring extreme performance, such as high-speed aircraft and heavily loaded mechanical structures.

2.2 The language of aluminum alloy status
The status mark of aluminum alloy is like a secret language, describing the heat treatment and processing history of the material, providing precise guidance for the performance and application of the material:
F state: original processing state, without excessive carving, retaining the original characteristics of the material, suitable for occasions where performance requirements are not particularly high.
O state: Soft after annealing, like a newborn baby, with the highest plasticity, suitable for applications requiring deep processing, such as bending, stretching and forming.
W state: Natural aging after solution treatment, which is the transition of performance transformation and provides a certain stability to the material. It is suitable for applications that require a certain strength but do not want to be too hard and brittle.
H state: The embodiment of work hardening. Different degrees of hardening treatment make the material more personalized and suitable for applications requiring specific strength and hardness, such as precision parts and structural parts.
T state: The ultimate secret of heat treatment, through precise control, it reaches the peak of material performance. It is suitable for occasions with extremely high performance requirements, such as aerospace and military equipment.
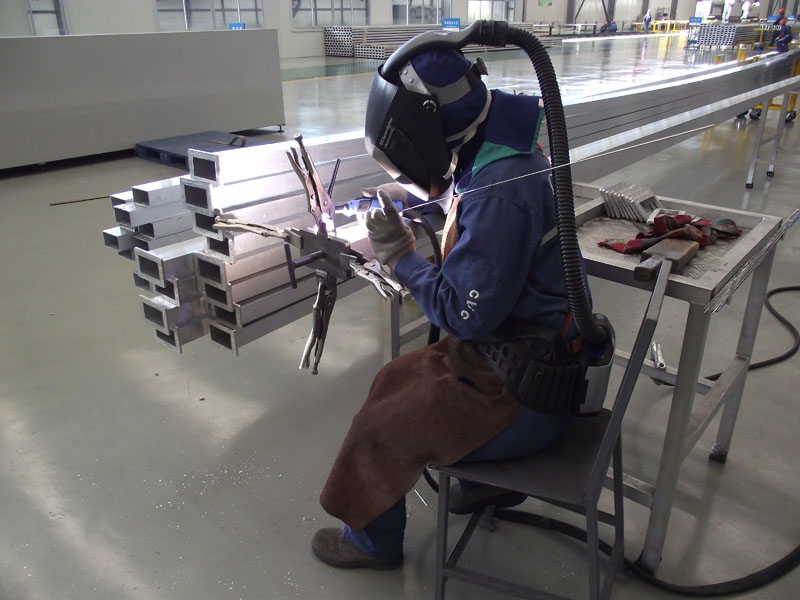
Innovation in aluminum alloy welding technology
Aluminum alloy welding technology is a bridge connecting modern industry. Faced with challenges such as heat-affected zones, pores and deformation during aluminum alloy welding, engineers continue to explore and innovate to meet increasingly stringent industrial standards and performance requirements:
3.1 The Art of Welding
TIG welding: Tungsten inert gas shielded welding, with its precise energy control and high-quality welding results, has become a representative of high-end welding. This welding method can stably provide energy at high temperatures, ensure the strength and quality of welded joints, and is widely used in demanding aerospace fields.
MIG welding: Melting extremely inert gas shielded welding, with its efficient automation capabilities and adaptability to thick plate welding, has become a good helper in industrial production. This welding method achieves a fast and continuous welding process by continuously feeding the welding wire, and is suitable for mass production and automated lines.
Laser welding: Laser welding, with its high energy density and fine welding control, provides a perfect solution for the welding of precision components. This welding method can provide huge energy in a tiny area, achieve high-precision and high-quality welding, and is suitable for precision manufacturing fields such as electronics and medical equipment.
Application areas of aluminum alloys
The application of aluminum alloy is like a colorful picture, displayed in various industrial fields:
Aviation industry: The lightweight and high-strength properties of aluminum alloys make them a favorite in aircraft manufacturing. From commercial airliners to military fighter jets, aluminum alloys play a key role in reducing structural weight, improving fuel efficiency and increasing airframe strength.
Automobile industry: In pursuit of higher fuel efficiency and lower emissions, aluminum alloys play an increasingly important role in automobile manufacturing. From engine components to body structures, the use of aluminum alloys helps reduce vehicle weight and improve performance and safety.
Construction Industry: The corrosion resistance and aesthetic properties of aluminum alloys make them popular in the construction sector. Whether used as door and window frames or curtain wall systems, aluminum alloys provide long-term performance guarantees and elegant appearance.
Electronic industry: The excellent electrical conductivity and heat dissipation properties of aluminum alloy make it play an indispensable role in electronic equipment. From mobile phone cases to computer radiators, aluminum alloys are ideal for improving device performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Aluminum alloy occupies an irreplaceable position in modern industry with its unique properties and broad application prospects. With the advancement of welding technology, the application potential of aluminum alloys will be further explored and realized. We look forward to aluminum alloys shining brighter in future industrial development and contributing more to the progress of human society.